Public Cloud and Industry Cloud: What businesses must know?
Cloud has become a strategic advantage for companies to optimize performance. Developments in high performance computing further add to capabilities that enable enterprises to leverage Artificial Intelligence and machine learning at scale.
In the year 2021, if you are evaluating whether to embrace cloud migration, you are already behind a lot of companies. A vast number of companies are not only replatforming applications to the cloud, they are deploying a hybrid cloud model, using a multi-cloud approach. Cloud adoption is no more a discussion but an actionable priority for Enterprises.
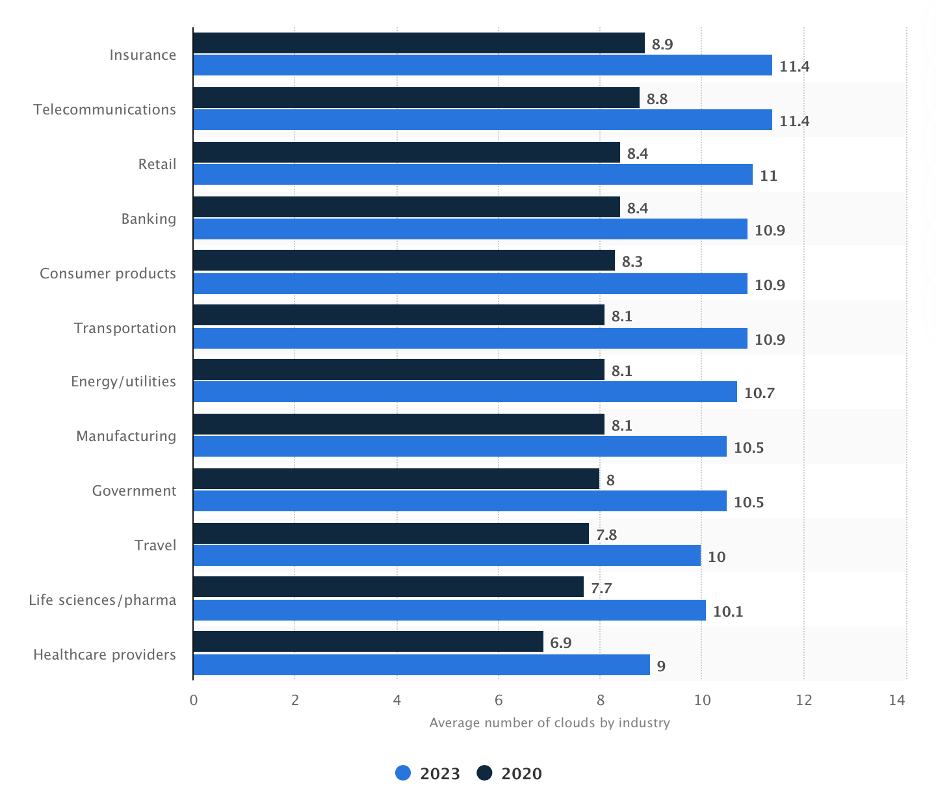
Today, companies across industries are leveraging around eight clouds from multiple vendors. – Statista
There are many reasons why enterprises are choosing the cloud over conventional ways of computing and data storage. Just like any other technology, cloud migration also comes with many options. While public cloud has been in use by companies for a long time, lately they have started considering industry cloud as well. There are various factors encouraging companies to move from their legacy on-premises facilities to the cloud.
Worldwide Public Cloud Services End-User Spending Forecast
(Millions of U.S. Dollars)
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| Cloud Business Process Services (BPaaS) | 46,131 | 50,165 | 53,121 |
| Cloud Application Infrastructure Services (PaaS) | 46,335 | 59,451 | 71,525 |
| Cloud Application Services (SaaS) | 102,798 | 122,633 | 145,377 |
| Cloud Management and Security Services | 14,323 | 16,029 | 18,006 |
| Cloud Infrastructure Services (IaaS) | 59,225 | 82,023 | 106,800 |
| Desktop as a Service (DaaS) | 1,220 | 2,046 | 2,667 |
| Total Market | 270,033 | 332,349 | 397,496 |
| BPaaS= business process as a service; IaaS= infrastructure as a service; PaaS= platform as a service; SaaS= software as a service; |
Source: Gartner (April 2021) | ||
But, which one should businesses select – industry cloud or public cloud?
Before we jump to the present state of cloud computing solutions, let us walk you through the difference between the public and industry cloud.
Public cloud – what’s that?
Public cloud is a shared platform that is accessible to the public through an Internet connection from any device, anywhere and anytime. It is operated on the pay-as-a-use model and administered by a cloud service provider.
A public cloud is a substitute to legacy on-premises IT architectures. In the case of a public cloud computing model, a third-party provider hosts easily scalable, on-demand IT resources and provides them to users over public internet or a specified network.
Some of the leading public cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, and Google Cloud.
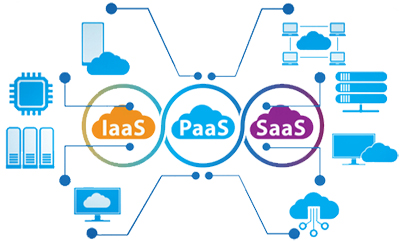
Both public and private cloud are offering three service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Benefits
- Accessibility– Easily accessible everywhere via the public Internet.
- Scalability- On-demand resources are available to meet your business needs.
- High reliability– A vast network of servers ensures against failure.
- Cost-effectiveness– With the ability to scale to the public cloud, you pay for extra computing power only when needed.
- Flexibility– You can take advantage of additional resources in the public cloud when you need them.
Key use cases:
 E-Commerce companies with dynamic requirements can keep their services elastic and can seamlessly scale offerings temporarily for the Christmas season. They only need to pay for the capacities booked, unlike the in-house IT infrastructure. This results in significant cost saving.
E-Commerce companies with dynamic requirements can keep their services elastic and can seamlessly scale offerings temporarily for the Christmas season. They only need to pay for the capacities booked, unlike the in-house IT infrastructure. This results in significant cost saving.
![]() Public cloud ensures redundancy and high availability for critical services. For businesses having critical processes relying on few applications or IT systems, a single server failure can result in a major revenue loss. In a public cloud, the company can get a high availability feature, which it can activate when the need arises, until the original systems start functioning again.
Public cloud ensures redundancy and high availability for critical services. For businesses having critical processes relying on few applications or IT systems, a single server failure can result in a major revenue loss. In a public cloud, the company can get a high availability feature, which it can activate when the need arises, until the original systems start functioning again.
Industry cloud – What is it, then?
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the cloud shift, but not all organizations have considered public cloud adoption. Many businesses are moving to the industry cloud.
An industry cloud solution focuses on a specific business problem and offers a clear value proposition. Industry clouds are collections of cloud services, applications, and tools optimized for the mission-critical use cases in a specific industry. They promise customized capabilities for critical components such as APIs, common data models and workflows.
In fact, if you are investing in industry cloud solutions provided by major public cloud providers, you are likely to get a variety of software and services, including industry-specific applications, from partners.
Who can get benefitted from Industry Clouds?
Industry clouds are of interest mainly because of their potential to create value for customers as well as public cloud providers. These clouds are specifically beneficial for the established industry-focused companies that have been feeling the fierce competition from cloud-native disruptors.
Industry-specific companies face challenges in moving their core business applications to public cloud as they majorly rely on homegrown legacy applications or domain-focused software designed for on-premise data centers. They can’t just ‘lift and shift’ applications to the public cloud; and optimizing or rewriting them for the cloud becomes costly and time consuming.
Industry clouds hold the potential to take the risk out of cloud migrations for such companies. Unlike public cloud, industry cloud addresses the specific requirements of the domain it is designed to serve.
For instance,
Healthcare providers prioritize enhancing the patient experience but also need to maintain high levels of security, data protection, and privacy. They must comply with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations. Like healthcare, the financial services industry is also a highly regulated industry.
Similarly, different industries need to adhere to different regulations, which makes it challenging for industry-specific companies to move to the public cloud. This has helped industry cloud emerge as a lucrative space for enterprises with business operations in industries that are subject to data protection or retention regulations, have regulatory restrictions on software use that disallow the rapid changes prevalent to software development, etc.
Such requirements make public cloud solutions risky for domain-specific companies. This issue is also one of the key reasons why many established companies have fallen behind moving to the cloud so far.
As industry cloud represents efforts from conventional public cloud providers, like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, or Amazon Web Services (AWS) to provide tailored solutions to meet the industry-specific needs of organizations, the demand for this cloud is growing even more.
The Bottomline
Both the public and industry clouds have their set of benefits depending on your company’s needs. The pricing varies depending on the cloud service provider that you choose.
We hope this blog gave you a good idea and food for thought on the difference between the public and the industry cloud.
If you are seeking cloud assistance, you can explore opportunities with PureSoftware. We offer tailored hybrid cloud and managed services and mission-critical support to maximize the availability, performance, and value of cloud adoption. We are also a proud partner of top cloud service providers, including Oracle, Microsoft Azure and AWS. You can reach us at info@puresoftware.com.